| Issue |
J. Phys. IV France
Volume 126, June 2005
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 101 - 105 | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/jp4:2005126021 | |
J. Phys. IV France 126 (2005) 101-105
DOI: 10.1051/jp4:2005126021
Raman spectroscopy and X-ray diffraction of lithium niobate at
temperatures up to 1300
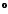 C
C
B. Moulin1, 0, L. Hennet1, D. Thiaudière1, 2, P. Melin1 and P. Simon1 1 CRMHT-CNRS, 45071 Orléans Cedex 2, France
2 LURE, Centre Universitaire Paris-Sud, Bât. 209D, BP. 34, 91898 Orsay Cedex and Synchrotron Soleil, l'Orme des Merisiers, Saint-Aubin, BP. 48, 91192 Gif-sur-Yvette Cedex, France
Abstract
Lithium niobate has been studied above its melting point
by X-ray diffraction and Raman micro-spectroscopy. For two compositions
(congruent and 54 mol% Li2O), a strange phenomenon occurs, starting
approximately 10![]() C above melting: solid clusters (30
C above melting: solid clusters (30 ![]() m) appear in
the liquid, remaining up to higher temperatures. These clusters are
identified as ferroelectric lithium niobate by means of Raman and X-ray
investigations.
m) appear in
the liquid, remaining up to higher temperatures. These clusters are
identified as ferroelectric lithium niobate by means of Raman and X-ray
investigations.
© EDP Sciences 2005



