| Numéro |
J. Phys. IV France
Volume 112, October 2003
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 533 - 536 | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/jp4:2003941 | |
J. Phys. IV France 112 (2003) 533
DOI: 10.1051/jp4:2003941
Generation of aligned
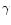 precipitates in Cu-Zn-Al single crystals
precipitates in Cu-Zn-Al single crystals
M.L. Castro1, J. Pons2 and E. Cesari2
1 IFIMAT, Facultad de Ciencias Exactas, Universidad Nacional del Centro de la Provincia de Buenos Aires, Pinto 399, 7000 Tandil, Argentina
2 Departament de Fisica, Universitat de les llles Balears, Ctra. de Valldemossa km. 7.5, 07071 Palma de Mallorca, Spain
Abstract
Several thermal treatments are known from literature to generate different distributions of y phase precipitates in Cu-Zn-Al
alloys with martensitic transformation temperatures below room temperature. Some of these treatments are composed of a first
quench followed by a flash heating to 670K for different times up to hundreds of seconds. The same type of treatments have
been used in a Cu - 12.7Zn - 17.7Al ailoy (% at, e/a = 1.48) with a nominal Ms of 320 K, in order to study the influence of
the precipitates on the martensite stabilization. In step-quenched specimens, the martensite stabilization by quenching was
small and the precipitates obtained after the flash heating were homogeneously distributed, like in the alloys with low transformation
temperatures. However, the specimens directly quenched to martensite exhibited a strong stabilization degree. After the subsequent
flash heating, the distributions of precipitates clearly showed particular alignments along the boundaries of the martensite
plates existing before the flash heating, as well as along the basal plane of certain martensite plates. In the present work
the characteristics and mechanisms of formation of these particular distributions of precipitates will be discussed.
© EDP Sciences 2003



